First In First Out
In an operating system that uses paging for memory management, a page replacement algorithm is needed to
decide which page needs to be replaced when a new page comes in.
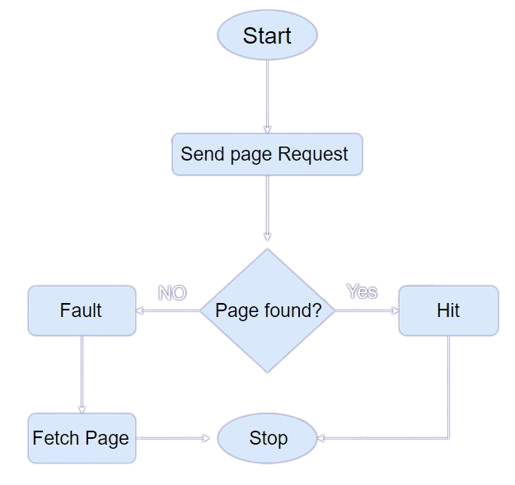
Page Fault: A page fault happens when a running program accesses a memory page that is
mapped
into the
virtual address space but not loaded in physical memory. Since actual physical memory is much smaller
than virtual memory, page faults happen. In case of a page fault, Operating System might have to replace
one of the existing pages with the newly needed page. Different page replacement algorithms suggest
different ways to decide which page to replace. The target for all algorithms is to reduce the number of
page faults.
First In First Out (FIFO): This is a popular page replacement
algorithm in operating systems. The basic idea behind FIFO is that the page that has been in the memory
the longest should be the one to be replaced. In other words, the page that was brought into memory
first should be the first one to be replaced when the memory is full.
The implementation of the FIFO algorithm is quite simple. The operating system maintains a queue of
pages in the memory. Whenever a new page is brought into memory, it is added to the end of the queue.
When the memory is full and a new page needs to be brought in, the page at the front of the queue is
replaced.